Introduction: Understanding Rotary Dampers
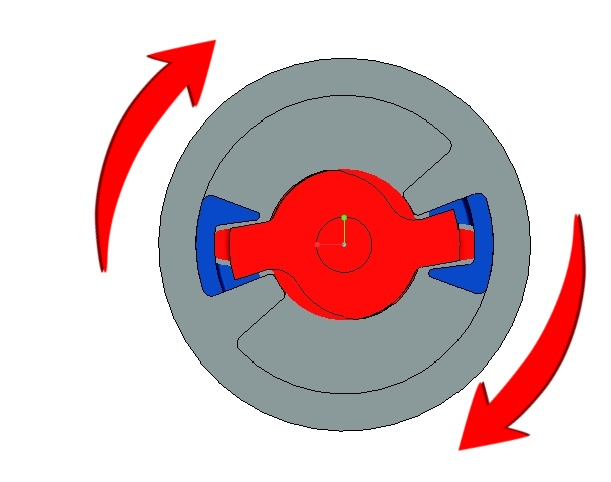
Rotary dampers are essential components designed for soft-close applications, ensuring controlled motion and enhanced user experience. Rotary dampers can be further classified into Vane Dampers, Barrel Dampers, Gear Dampers, and Disk Dampers, each representing a different type of rotary damper designed for specific applications.Rotary dampers use viscous fluid resistance to regulate speed and smooth movement. When external force rotates the damper, the internal fluid generates resistance, slowing down the motion.
From soft-close toilet seats to premium automotive interiors, washing machines, and high-end furniture, rotary dampers are widely used to improve product functionality. They ensure quiet, smooth, and controlled motion, extending the lifespan of products while enhancing their usability. But how do rotary dampers work? Where are they used? And why should they be integrated into product designs? Let's explore.
How Does a Rotary Damper Work?
A rotary damper works through a simple yet effective mechanism:
● External force is applied, causing the damper to rotate.
● Internal fluid generates resistance, slowing down the motion.
● Controlled, smooth, and noise-free movement is achieved.
Comparison: Rotary Damper vs. Hydraulic Damper vs. Friction Dampe
|
Type |
Working Principle |
Resistance Characteristics |
Applications |
|
Rotary Damper |
Uses viscous fluid or magnetic eddy currents to create resistance when the shaft rotates. |
Resistance varies with speed—higher speed, greater resistance. |
Soft-close toilet lids, washing machine covers, automotive consoles, industrial enclosures. |
|
Hydraulic Damper |
Utilizes hydraulic oil passing through small valves to create resistance. |
Resistance is proportional to the square of velocity, meaning significant changes with speed variation. |
Automotive suspension, industrial machinery, aerospace damping systems. |
|
Friction Damper |
Generates resistance through friction between surfaces. |
Resistance depends on contact pressure and friction coefficient; less affected by speed variations. |
Soft-close furniture hinges, mechanical control systems, and vibration absorption. |
Key Benefits of Rotary Dampers
● Smooth, controlled motion —Enhances product safety and usability.
● Noise reduction —Improves user experience and brand perception.
● Extended product lifespan —Reduces maintenance costs and improves reliability.
For brand owners, rotary dampers are compact, making it easy to integrate them into existing product designs with minimal upgrade costs. However, incorporating a soft-close design not only enhances the product with the above advantages but also creates differentiating selling points, such as “silent close” and “anti-scald design.” These features serve as strong marketing highlights, significantly boosting the product’s appeal and competitiveness.
Applications of Rotary Dampers
● Automotive Industry —Glove compartments, cup holders, armrests, center consoles, luxury interiors and so on
● Home and Furniture —Soft-close toilet seats, kitchen cabinets, dishwashers, high-end appliance lids and so on
● Medical Equipment —ICU hospital beds, surgical tables, diagnostic machines, MRI scanner components and so on
● Industrial & Electronics — Camera stabilizers, robotic arms, lab instruments and so on
Toyou damper for Washing Machine
Toyou damper for Automotive Interior Door Handles
ToYou Damper for Car Interior Grab Handles
ToYou Damper for hospital beds
ToYou Damper for Auditorium chairs
How to Choose the Right Rotary Damper?
Selecting the best rotary damper for your application requires careful evaluation of various factors:
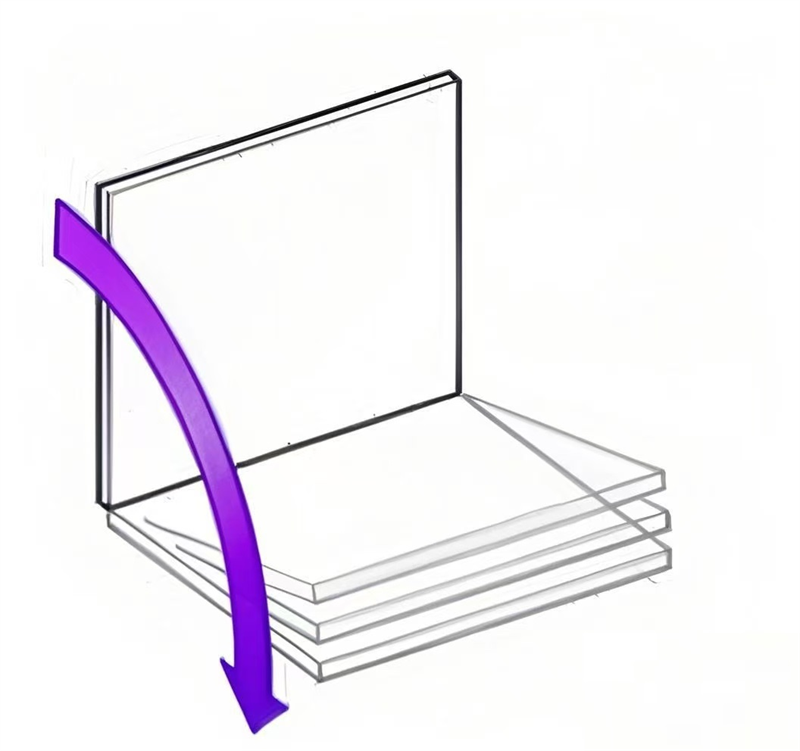
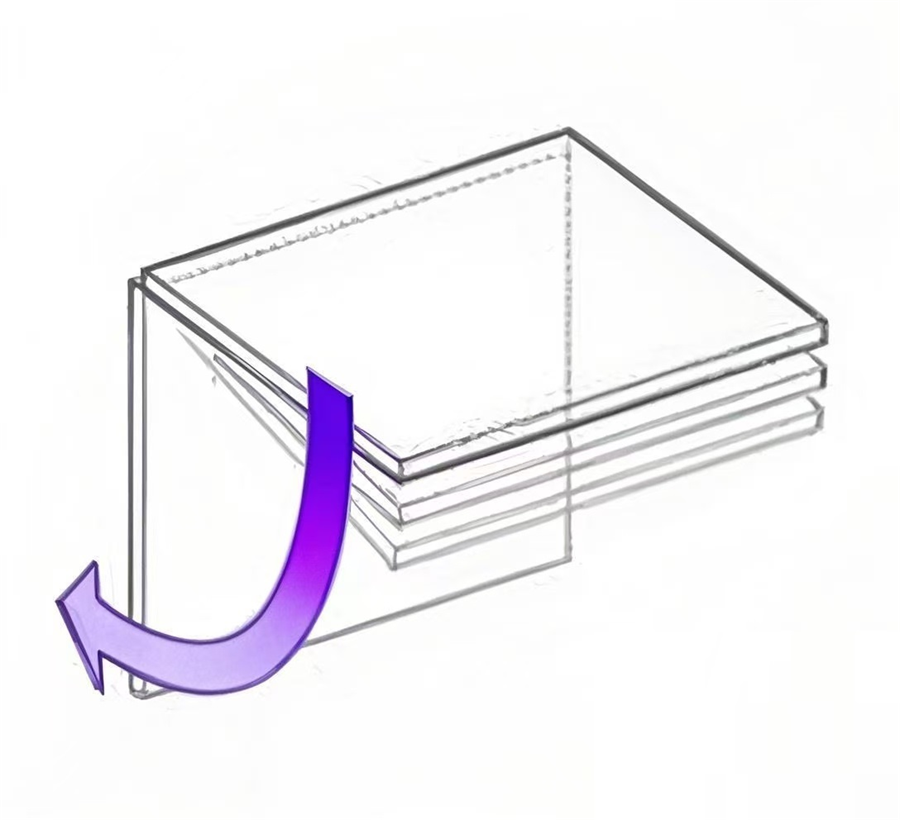
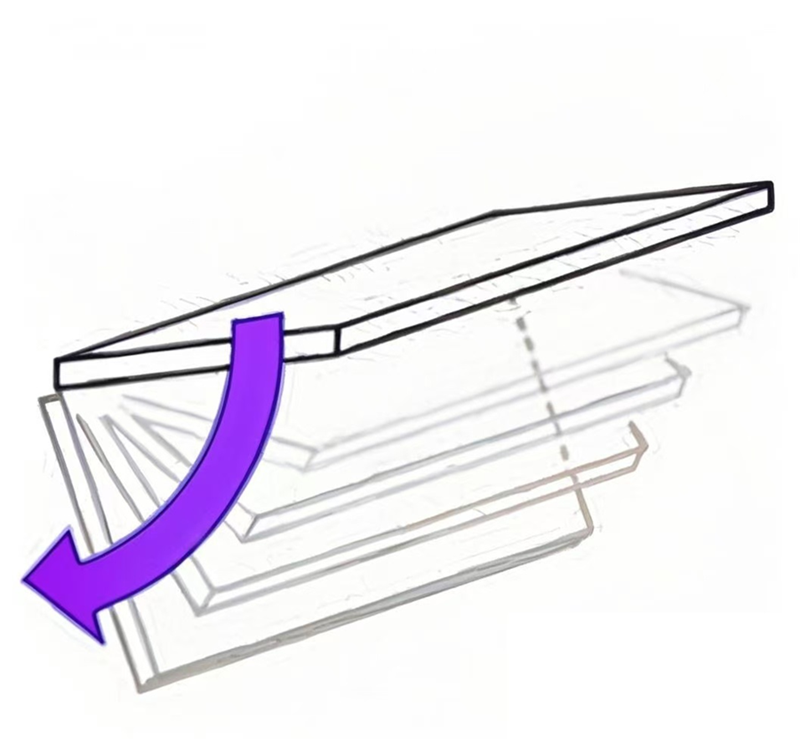
Step 1: Determine the type of motion required for the application.
Horizontal use
Vertical use
Horizontal & Vertical use
Step 2:Determine the Damping Torque
● Analyze Load Conditions, including weight, size, and motion inertia.
Weight: How heavy is the component that needs support? For example, is the lid 1kg or 5kg?
Size: Is the component affected by the damper long or large? A longer lid may require a higher torque damper.
Motion Inertia: Does the component generate significant impact during movement? For example, when closing a car glove box, the inertia may be high, requiring greater damping torque to control the speed.
● Calculate Torque
The formula for torque calculation is:
Let’s take the TRD-N1 series as an example. The TRD-N1 is designed to generate high torque just before the lid fully closes when falling from a vertical position. This ensures a smooth and controlled closing motion, preventing sudden impacts (see Diagram A). However, if the lid closes from a horizontal position (see Diagram B), the damper will produce excessive resistance right before full closure, which may prevent the lid from closing properly.
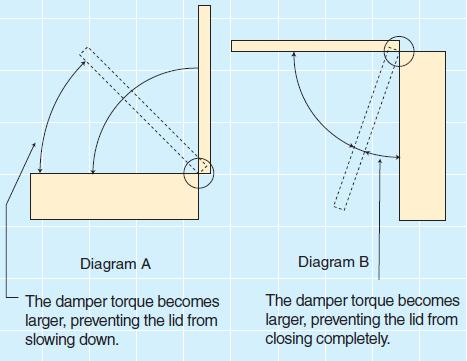
First, we need to confirm that our application involves a vertically falling lid rather than one that closes from a horizontal position. Since this is the case, we can proceed with using the TRD-N1 series.
Next, we calculate the required torque (T) to select the right TRD-N1 model. The formula is:
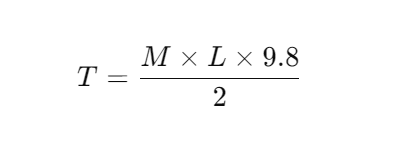
where T is the torque (N·m), M is the lid’s mass (kg), L is the lid’s length (m), 9.8 is the gravitational acceleration (m/s²), and the division by 2 accounts for the lid’s pivot point being at the center.
For example, if the lid has a mass M = 1.5 kg and a length L = 0.4 m, then the torque calculation is:
T=(1.5×0.4×9.8)÷2=2.94N⋅m
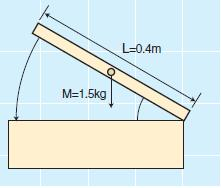

Based on this result, the TRD-N1-303 damper is the most suitable choice.
Step 3: Select the Damping Direction
● Unidirectional rotary dampers —Ideal for applications requiring damping in a single direction, such as soft-close toilet seats and printer covers.
● Bidirectional rotary dampers —Suitable for applications needing resistance in both directions, such as automotive armrests and adjustable medical beds.
Step 4: Confirm Installation Method and Dimensions
Ensure the rotary damper fits within the product’s design constraints.
Choose the appropriate mounting style: insert type, flange type, or embedded design.
Step 5: Consider Environmental Factors
● Temperature range — Ensure stable performance in extreme temperatures (e.g., -20°C to 80°C).
● Durability requirements —Select high-cycle models for frequent use (e.g., 50,000+ cycles).
● Corrosion resistance —Opt for moisture-resistant materials for outdoor, medical, or marine applications.
For a tailored motion control damper solution, consult our experienced engineers to design a custom rotary damper for your specific needs.
FAQs About Rotary Dampers
More questions about rotary dampers, such as
● What is the difference between unidirectional and bidirectional rotary dampers?
● Why do rotary dampers use damping oil?
● What are push-push latches and how do they relate to dampers?
● What are linear hydraulic dampers?
● Can rotary damper torque be customized for specific applications?
● How do you install a rotary damper in furniture and appliances?
For more details, feel free to contact us for expert recommendations on soft-close damper solutions tailored to your needs.
Post time: Mar-18-2025











